
Our engagement
We actively engage in crucial means to improve asset management performance and maximize the benefits for beneficiaries.
We aim to create win-win relationships by conducting multifaceted investigations into the reasons why companies are unable to realize their intrinsic value and encouraging transformation to improve their problems, on an equal footing with the companies.
Engagement structure
The following three teams engage in a "trinity" approach to engagement.
This structure allows each team to delve into their respective sectors while fostering collaboration among the teams.
The Engagement Team
- Composed of fund managers and corporate research analysts. The team holds in-depth meetings with companies that are engaged in medium- to long-term investments.
Corporate Research Team
-
Composed of corporate research analysts.
The team conducts research and holds meetings related to corporate value, business strategy, ESG, etc.
Stewardship Team
- Composed of the Stewardship Section of the Responsible Investment Department.
Holding meetings focusing on major themes of ESG, including corporate governance, and the exercise of voting rights. - Passive engagement
Engagement
track record
Total number in 2024
* The number of cases by theme is counted
multiple times for each engagement.
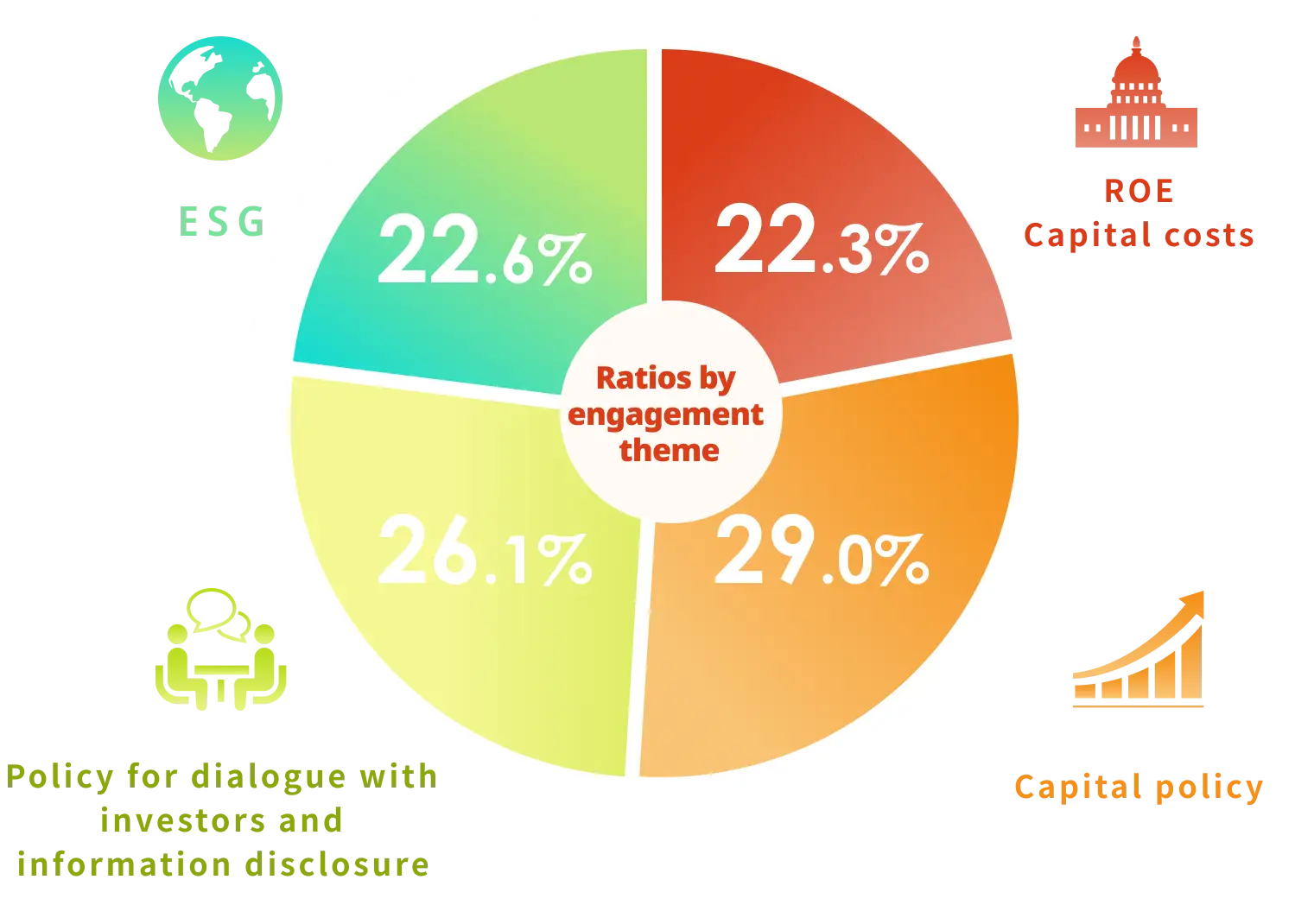
Our company's engagements
We categorize our engagements primarily into three types:

Strong engagement
This is an initiative aimed at significantly improving asset management performance by identifying engagement themes and directly and proactively encouraging the management teams of investee companies to address challenges directly.
This represents the deepest level of engagement activity.

Lingagement
(linkage + engagement)
Lingagement refers to activities that support the enhancement of corporate value by providing investee companies with a platform for discussions with other companies and promoting the sharing of knowledge.
This is our unique term that combines "linkage" and "engagement," both of which connect companies.
Passive engagement
Passive engagement refers to activities that involve dialogues in response to requests for meetings from investee companies and communicating our requests through letters and other means.
In order to further enhance the effectiveness of engagement, we conduct problem-solving dialogues related to ESG and other issues from our perspective.
Engagement process
Milestone management
In conducting strong engagement, we first set an engagement theme for each target company, and then create an engagement plan that summarizes the specific issues identified along with their background, issues to be addressed for resolution, and the anticipated situation after the issues are resolved.
The status of engagement is divided into the following five statuses for milestone management.
The progress is shared with analysts and fund managers, and regular monitoring is conducted by senior executives.
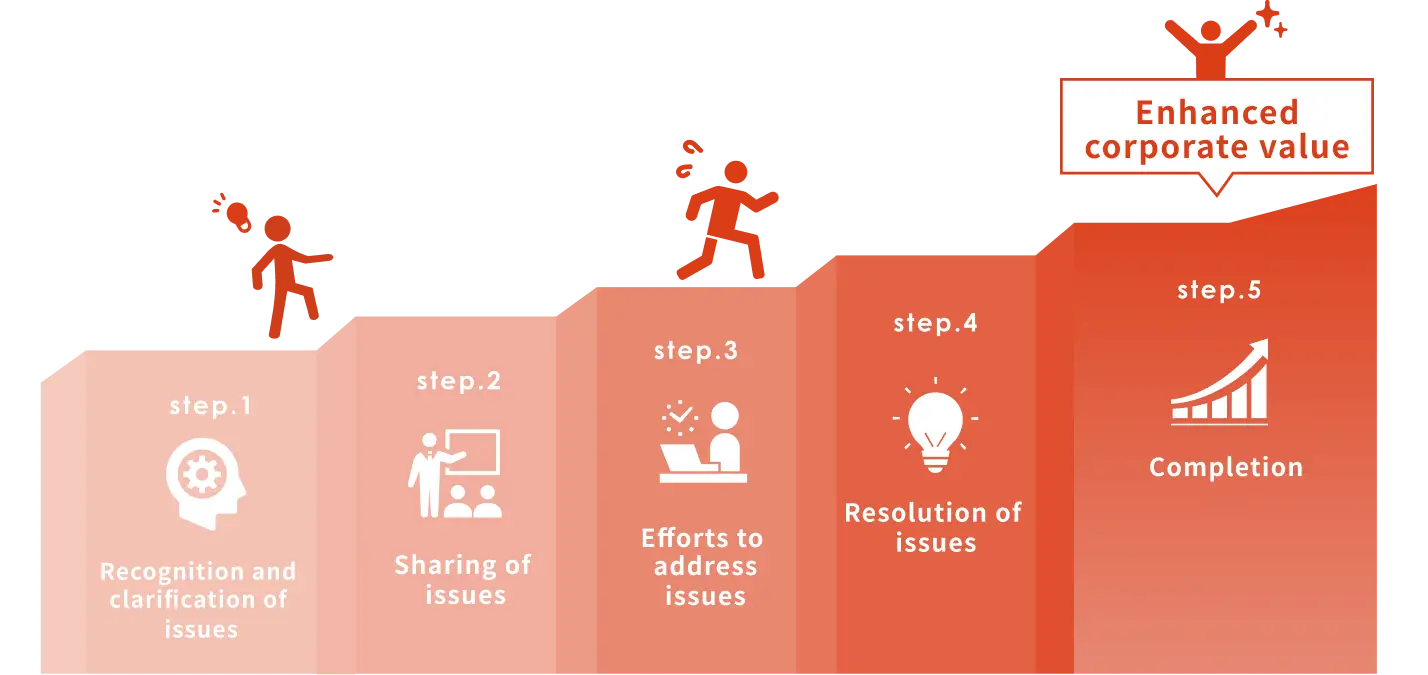
Examples of engagement
In passive engagement, we conduct engagement that focuses not only on the management and capital strategies of investee companies but also on improving materiality in our company.
The challenges faced by investee companies are diverse, with many being quite difficult to resolve. However, since passive asset management, in principle, does not allow for the option of selling holdings, we strive to engage in dialogues that can serve as a catalyst for sustainability and the enhancement of corporate value over the medium to long term.

Response to climate change by Company A
(glass, stone and clay products)
- Challenge
- Despite being a company with high CO2 emissions, their GHG emission reduction target is low.
- Background
- By proactively accelerating decarbonization, companies in high-emission sectors can significantly slow climate change, and their contributions can have a ripple effect on all stakeholders, ultimately leading to an increase in corporate value.
- Solution
- Setting the same standards as the government's targets as the minimum line, clarifying SBT certification acquisition and chronological countermeasures, and advancing initiatives that can be undertaken in the short term, such as switching to renewable energy for electricity.
The Company responded that it would review examples from domestic and overseas competitors and consider proactively implementing and disclosing feasible initiatives for further decarbonization.



Employee engagement at Company B
(electrical equipment company)
- Challenge
- The Company conducted its employee 's survey but has not yet disclosed specific details.
- Background
- Companies with high Employee's Engagement tend to have higher performance and productivity, so companies should actively disclose survey results and future plans as a starting point for formulating and implementing human capital strategies.
- Solution
- The Company should monitor the survey results using KPIs and disclose information that illustrates how they are implementing initiatives to resolve issues through a PDCA cycle.
Based on the feedback for the previous fiscal year, it set improving employee engagement as a materiality and a medium-term management target, and started disclosing specific details about its efforts regarding the results.


Directors' Term of Office in the articles of incorporation at Company C
(petroleum and coal products)
- Challenge
- The term of office for directors at The Company is two years, and the voices of shareholders cannot be reflected each year.
- Background
- Regarding management responsibilities, governance should be maintained with discipline by gaining the confidence of shareholders annually. If the term of office for directors is two years, shareholders cannot hold management accountable during the same fiscal year, even if a scandal occurs during a non-election period.
- Solution
- To shorten the term of office for directors in the articles of incorporation to one year.
It shortened the term of office for directors in the articles of incorporation from two years to one year, and updated its Corporate Governance Report accordingly.



Company D (marine transportation)
Decarbonization initiatives
- Issue
-
As the decarbonization of shipping companies requires both major
capital investment and the development of new technologies, presentation of a more concrete roadmap would facilitate understanding of the company’s situation by the market.
- Background
- While there is a necessity to appropriately reflect cost increases in freight rates subject to the understanding of clients when undertaking large-scale capital investments, the status of dialogs with clients and progress in the passing on of prices is not perceptible from the outside.
- Dialog content
-
The company’s investment plan significantly varies over the year.
Daiwa AM thus requested that the company gives indications of the situation,even in terms of major developments, such as the nature of the factors behind changes in investment planning and whether the cost increases stemming from decarbonization initiatives are being absorbed through price pass-on.
The company indicated that, although this will vary by client, there is a growing understanding of CO2 reduction with an awareness of Scope 3, particularly in the automotive industry, and that the business environment is steadily becoming more conducive to proactive investments in LNG- fueled vessels. They also stated that, while they will also regularly update their investment planning, they wish to take steps which will allow them to provide more detailed explanations of any changes to the content of their investment planning.



Company E (glass and ceramics products)
Gender diversity
- Issue
- The female manager ratio and the average years of service among female employees are low.
- Background
- While the low proportion of female employees is unavoidable due to the underlying background of low numbers of women with science and related backgrounds among technical employees at manufacturing sites, many female employees leave the company before they can be promoted to management positions, with problems also evident in terms of the company’s personnel system.
- Dialog content
- The lack of a sufficient education and training system and the failure to ensure diversity in workstyles (including the absence of a teleworking system and the existence of job relocations) can be considered problematic factors which lead female employees to leave the company. As well as improving these systems, it is desirable that the company increases its number of role models, including mid-career hires, and ensures that it provides more comprehensive support in areas such as career design.
The company is aware of the issues surrounding its personnel system and is considering measures such as the introduction of a teleworking system, institution of positions not subject to job relocations, and the enhancement of their training and education system as necessary.



Company F (construction)
Reduction of cross-shareholdings
- Issue
- The balance of cross-shareholdings is significantly above 20% of net assets but the pace at which these are being reduced remains slow.
- Background
- The balance of cross-shareholdings with business partners is considerable due to entrenched industry practices. In addition, the pace at which these are being sold has not increased due to the time required for discussions with counterparties.
- Dialog content
- As this industry is characterized by many counterparties asserting that the sale of their cross-shareholdings does not affect trading, the company should expedite the pace at which these are sold from the perspective of improving capital efficiency. At the same time, it should set targets to achieve less than 20% of cross-shareholdings to net assets.
The company stated that they would like to continue to hold repeated and detailed discussions with counterparties on the sale of cross- shareholdings but would like to be allowed to give further consideration regarding the setting of targets.

2025年
Regarding cases of escalation to the exercise of voting rights, please refer to the Proxy Voting Policy page.
For examples of strong engagement, see the Corporate Transformation Engagement page.



